PERFORATED PLATES - PERFORATION
DEFINITION PERFORATIONS
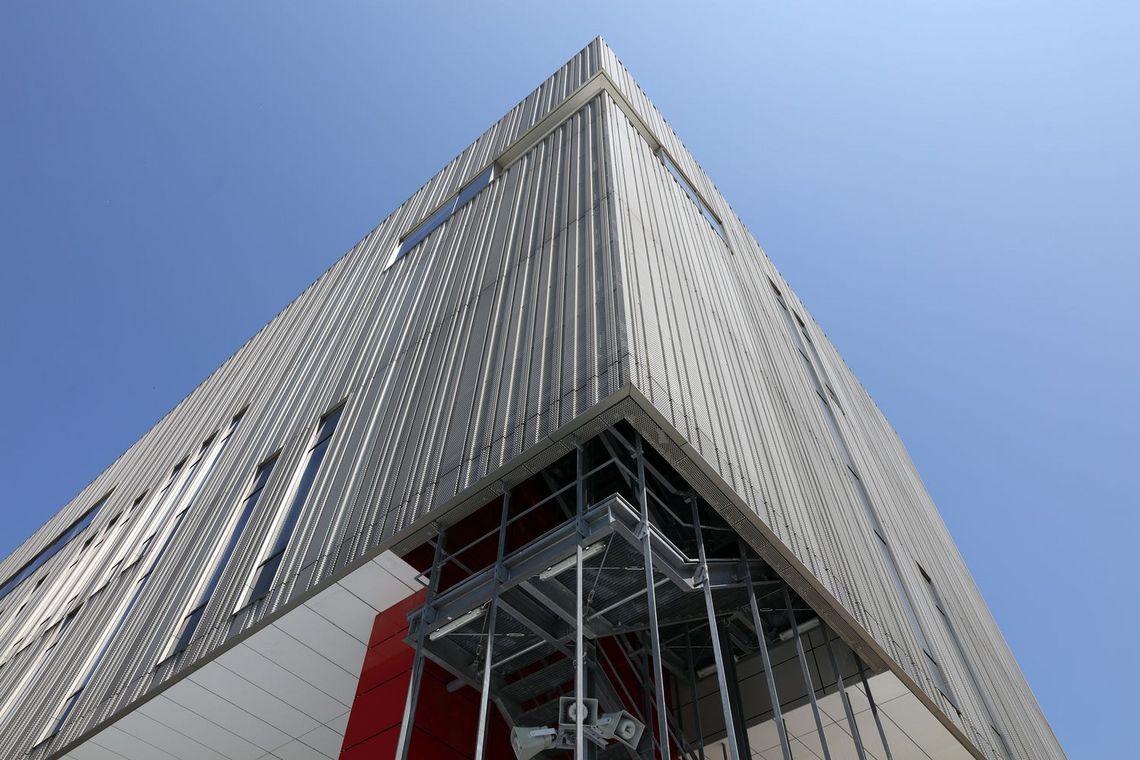
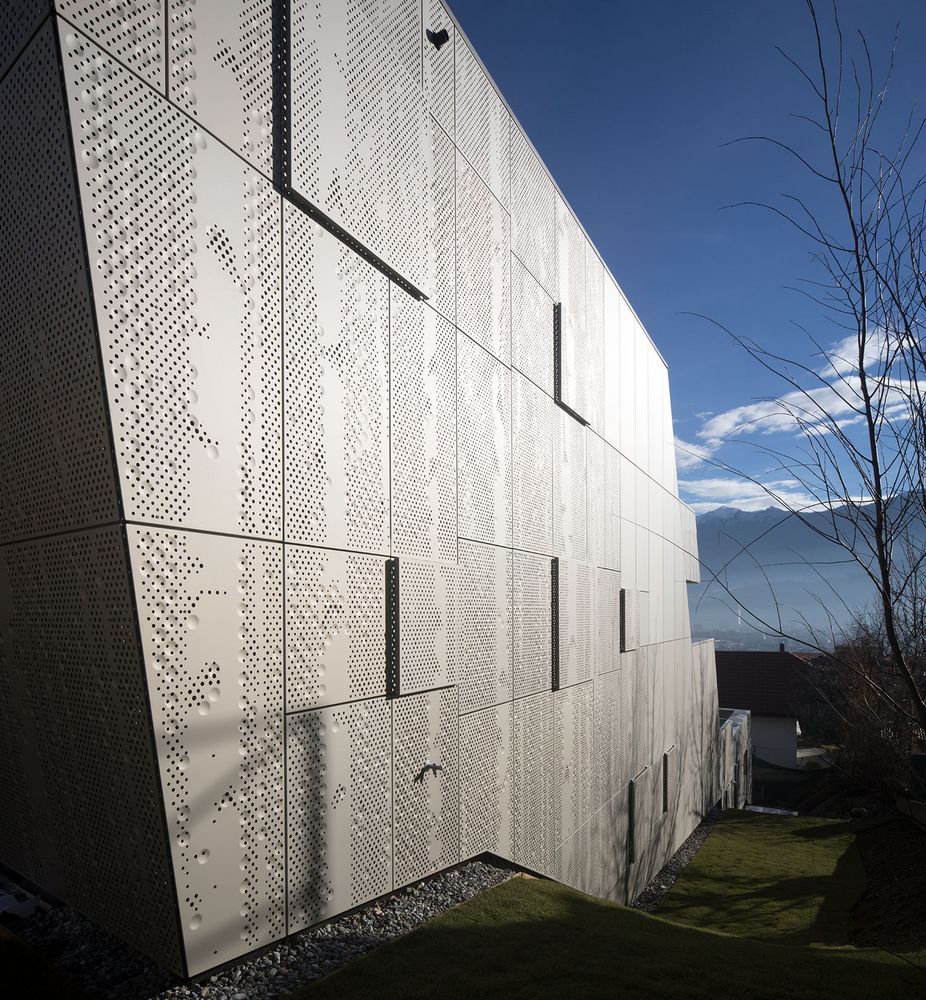
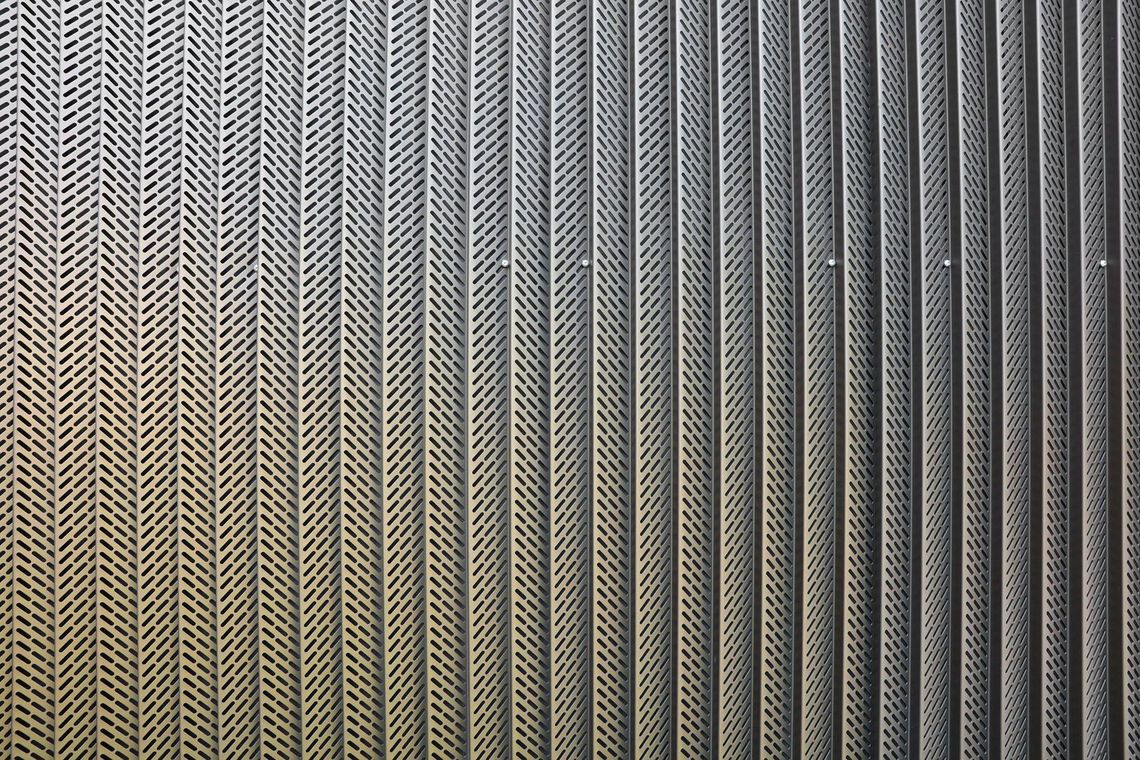
The term "perforated plate" (in practice usually referred to as perforated sheet or perforated plate) is defined in DIN 24041 and DIN 4184/Part 2. The perforated plate according to the aforementioned DIN standards thereby designates a plate (sheet, panel, etc.) with similar openings (holes) at regular intervals, which are produced e.g. by punching.
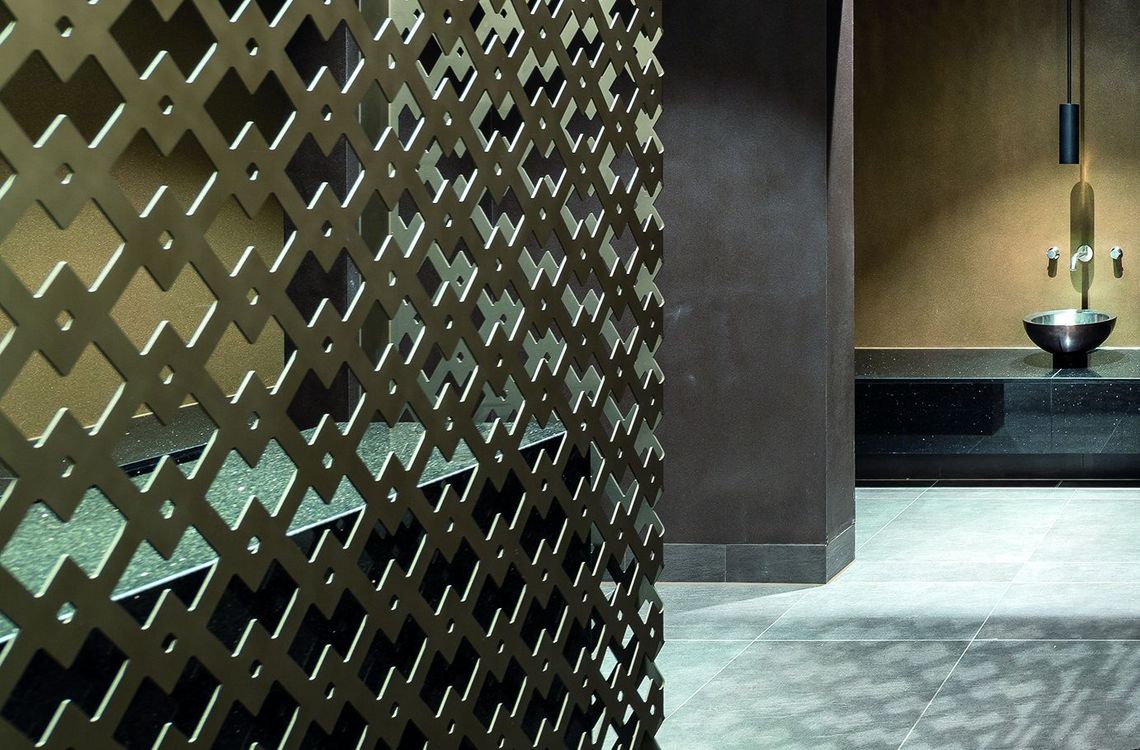
In deviation from these standards, plates with irregular holes and arrangements are also produced.
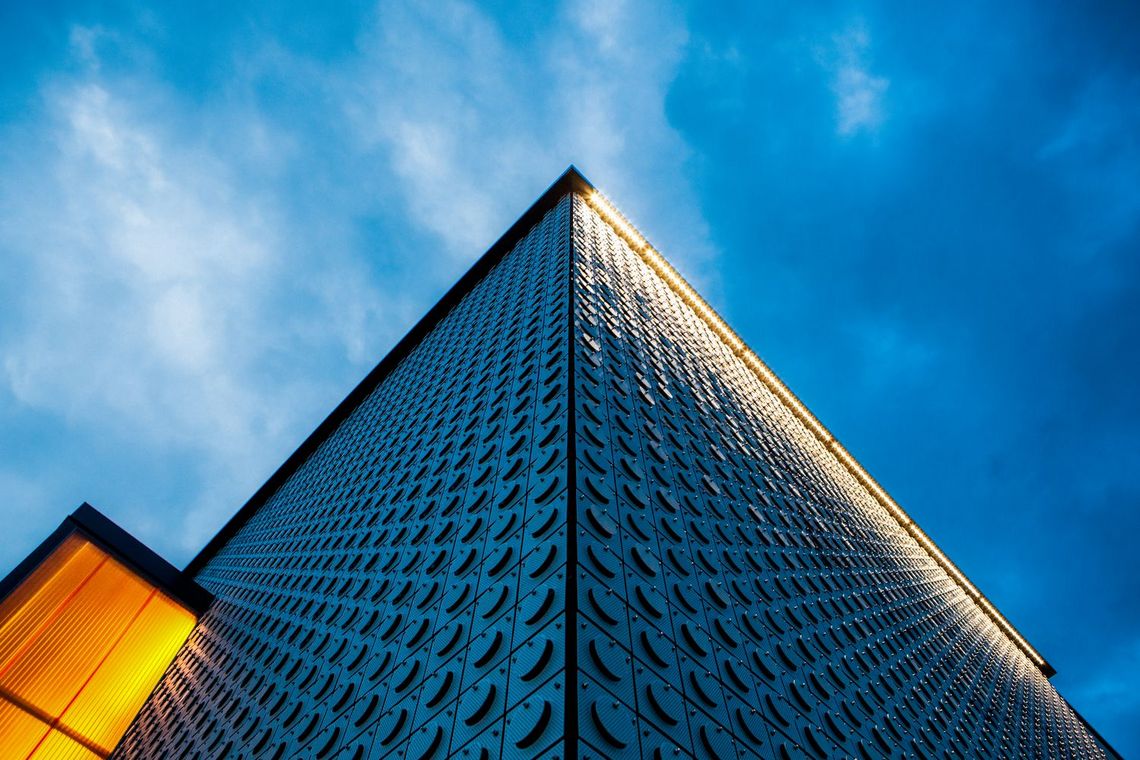
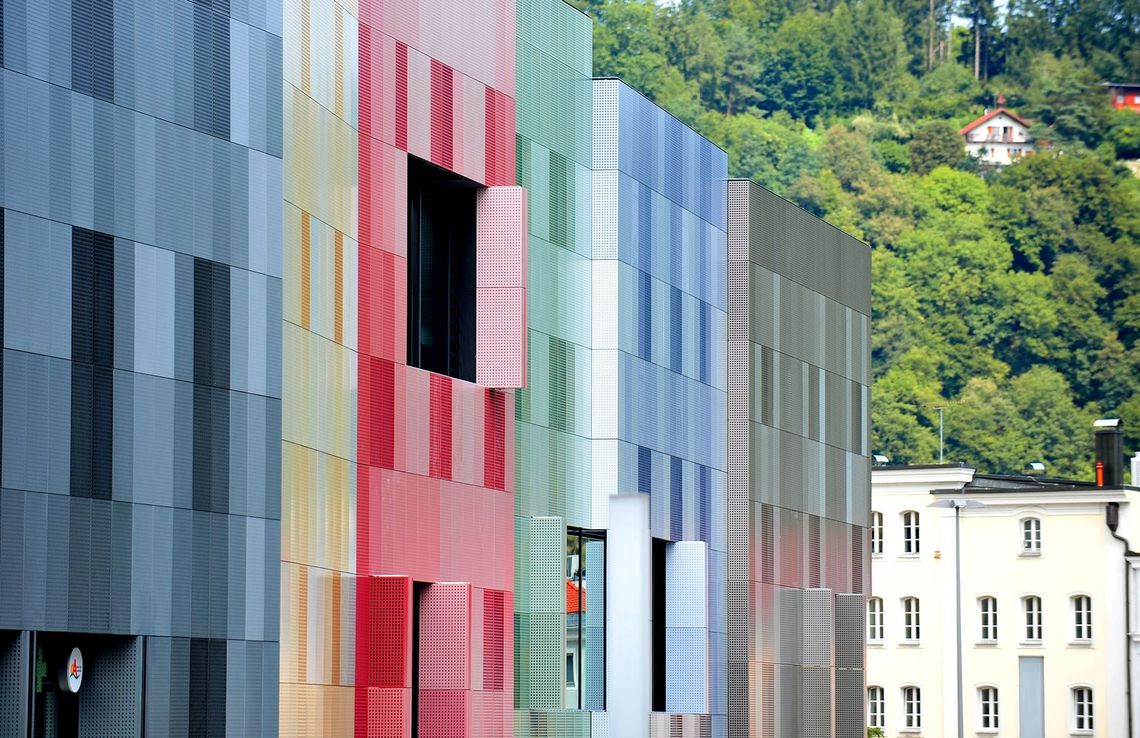
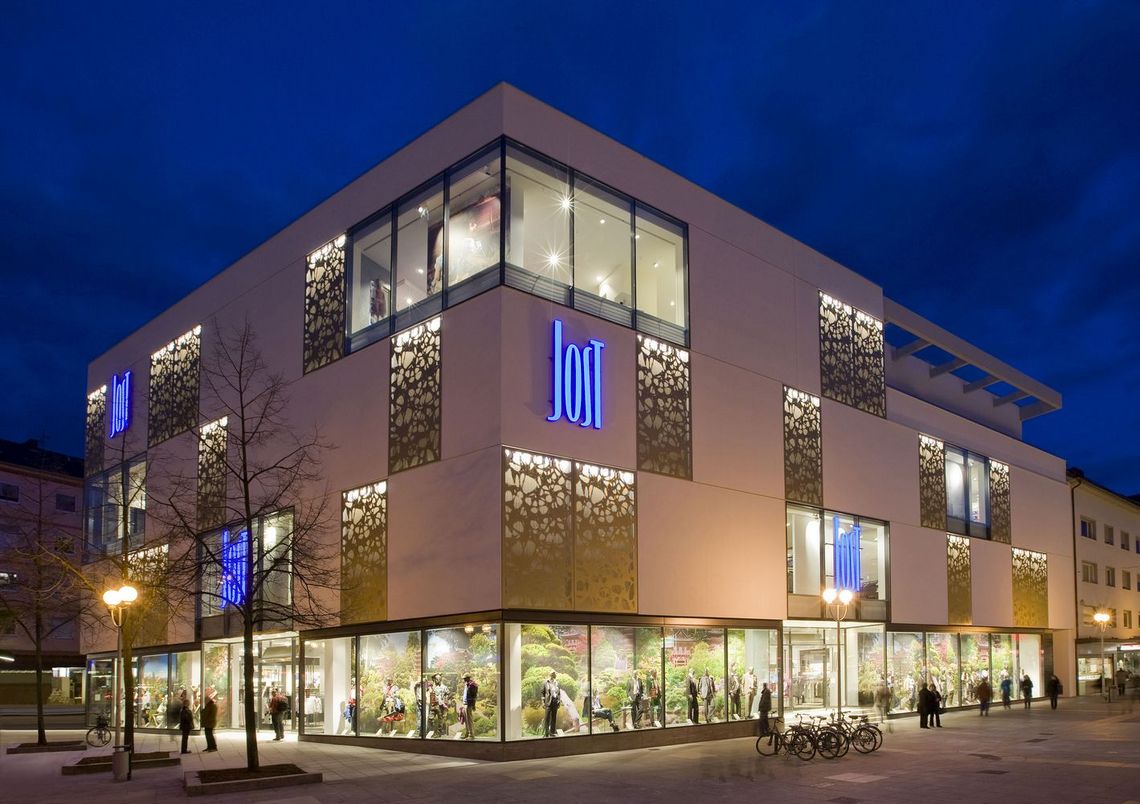
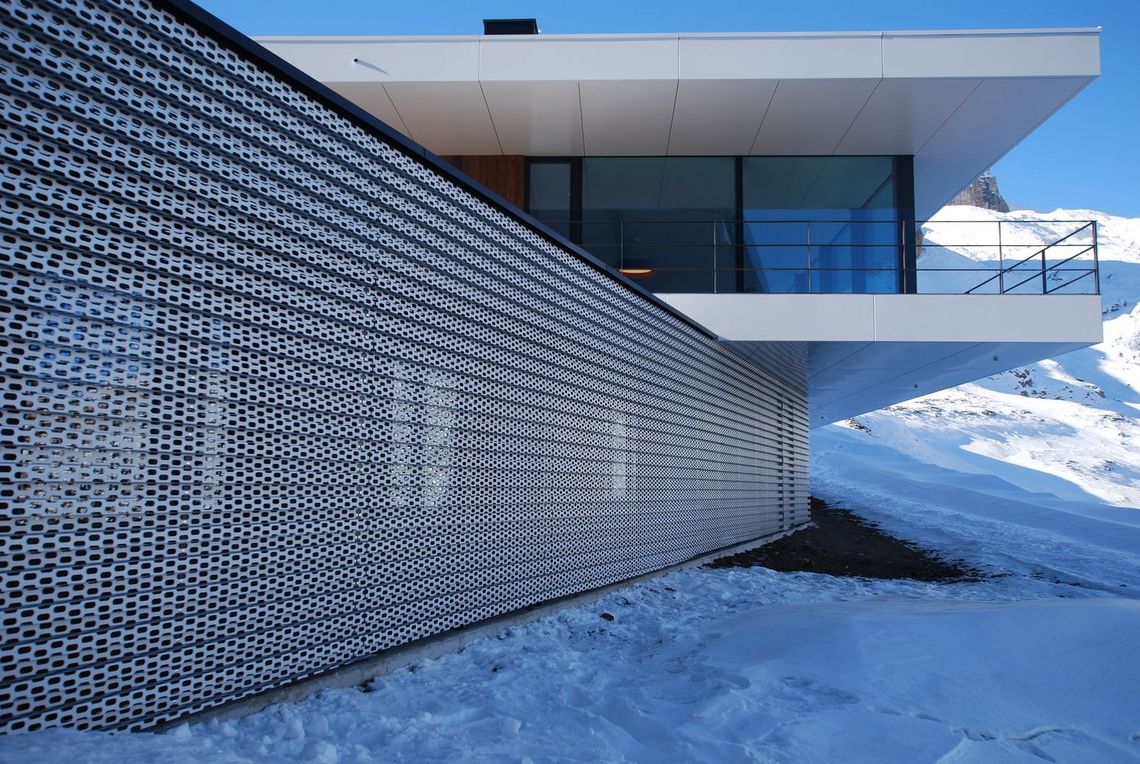
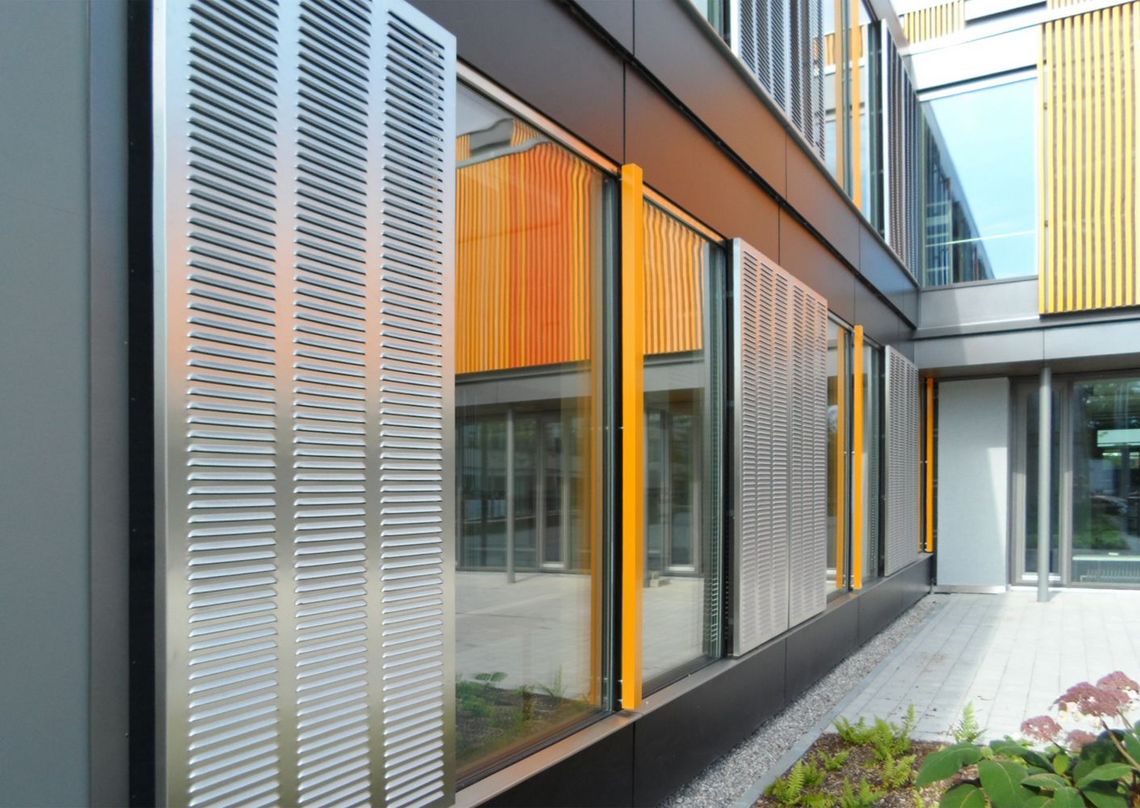
The best known hole shapes are arranged according to their geometry, from round to elliptical. In addition, there are a large number of special shapes, shown under decorative perforations or Deco + Design, which are used for a wide variety of applications.
PUNCH-IN/PUNCH-OUT SIDE
During the punching process, a distinction is made between the punch entry side (punch-in side) and the punch-out side.
On the punch-in side, a slight feed radius is formed, on the punch-out side, a punch burr is formed. The punch-in side is usually defined as the good side, on the reverse side a slight burr results.
FREE CROSS SECTION A0
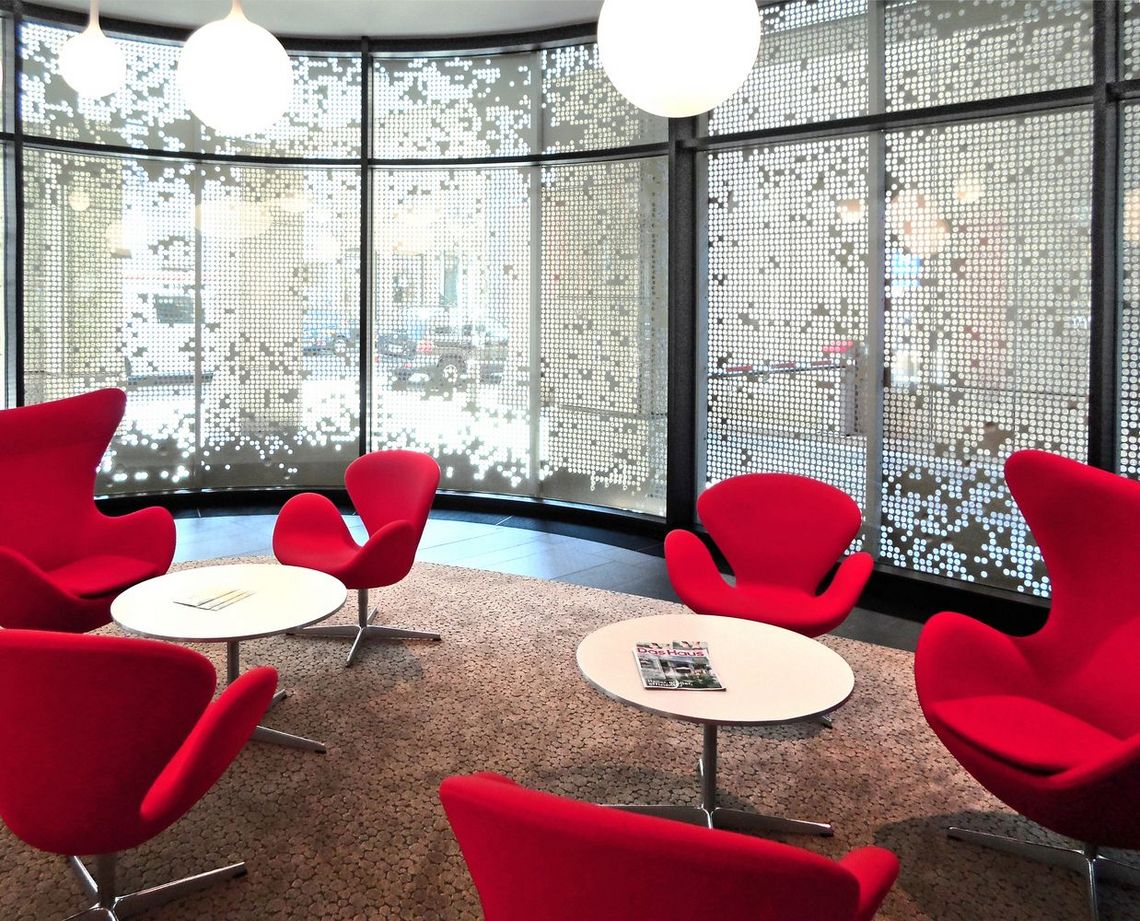
This means the relative free hole area (air passage), given in %. This depends on the type of perforation, the hole diameter and the ratio of the diameter to the pitch. A larger diameter does not automatically imply a higher A0. In practice, this not only determines the air permeability in technical use, but also the transparency in decorative use.
Example of offset round perforation:
Ø mm Pitch mm A0 in %
4 6 40
10 15 40
10 20
Depending on the application, different free cross-sections are required. By selecting the appropriate perforation, almost all specifications can be achieved.